Which Destination Address is Used in an Arp Request Frame
A MAC address table sometimes called a Content Addressable Memory CAM table is used on Ethernet switches to determine where to forward traffic on a LAN. On the transmit side it is typically transmitted as the source address of an Ethernet frame.
Reverse ARP RARP - It is a networking protocol used by the client system in a local area network LAN to request its IPv4 address from the ARP gateway router table.

. The size of the ARP message depends on the upper layer and lower layer address sizes which are given by the type of networking protocol usually IPv4 in use and the type of hardware or virtual link layer that the upper layer protocol is running on. If there is an ARP entry for the destination virtual machines IP address in the source virtual machines ARP table the MAC address from this entry is used. Now lets break this down a little bit to understand how the MAC address table is built and used by an Ethernet switch to help traffic move along the path to its destination.
A frame is encapsulated with source and destination MAC addresses. The physical address is assigned when the device is manufactured and cannot be changed. The ARP Request is an ARP payload carried within the appropriate L2 frame for the medium in use.
When a frame is sent to a device not on the local network the gateways MAC address is used in the frame header. When sending a packet to a remote destination a host will need to send the packet to a gateway on the local subnet. The ARP request packet is then encapsulated in an Ethernet frame with the MAC address of Host A as the source address and a broadcast FFFFFFFFFFFF as the destination address.
The source device will not know the MAC address of the remote host. When the ARP message is not an ARP request or when the ARP request isnt for an IP address on an Ethernet network it is ignored by this target. The majority of the time this will be Ethernet which will also be the L2 medium we will be looking at in our examples.
The Address Resolution Protocol uses a simple message format containing one address resolution request or response. --arp-mac-src address. The sending device will send an ARP request broadcast frame on to the network asking for the MAC address of the intended recipient based on the IP address of the destination.
The holder of that IP address will respond to the sender advertising the MAC address. The gateway address must be configured. Since the ARP request is a broadcast it reaches all the nodes in the Subnet A which includes the e0 interface of the router but does not reach Host D.
It also checks whether the host is using the original IP address or a duplicate one. ARP IP destination address specification. The gratuitous ARP is used to update the ARP table of other devices.
The physical gateway address is called the media access controlMAC address or burned in address BIA. When creating an IP forwarding virtual server as with all virtual servers you can create either a host IP forwarding virtual server which forwards traffic for a single host address or a network IP. MAC Address Tables.
The destination address in a received Ethernet frame to determine if the frame should be received or not. It dynamically maps local DHCP or remote IP addresses when you configure frame relay. The protocol field of the Ethernet frame can be used to denote the length of the header 80228023 networks.
A table is created by. How to Use ARP. ARP Command is a TCPIP utility used for viewing and modifying the local Address Resolution Protocol ARP cache.
An ARP request will be sent by the source and will be responded to by the router. Switch will forward the frame out all interfaces except the incoming interface. Because the gateway will be the Layer 2 destination for the frame on this LAN segment the destination MAC address must be the address of.
If the destination address is on a different network the source host will use. A Destination MAC address a Source MAC address and an EtherType. The ARP request packet is then encapsulated in an Ethernet frame with the MAC address of Host A as the source address and a broadcast FFFFFFFFFFFF as the destination address.
The Ethernet header will include three fields. Layer 2 broadcast means that frame will be sent to all hosts in the same layer 2 broadcast domain which includes the ether0 interface of the router but does not. In order to find out the MAC address of host B host A sends an ARP request listing the host Bs IP address as the destination IP address and the MAC address of FFFFFFFFFFFF Ethernet broadcast.
The router will respond with the MAC address of its interface the one which is connected to the same network as the. If an entry does not exist the source virtual machine will send an ARP broadcast with a request for the MAC address corresponding to the destination virtual machines IP address to be. It will send an ARP request to the DNS server for the destination MAC address.
When using inverse ARP we know the DLCI or remote router but dont know its IP address. Transmit Buffer Logical portion of the packet buffer used to store packets to be transmitted. Address translation is disabled when you create an IP forwarding virtual server leaving the destination address in the packet unchanged.
The Tcp Ip Guide Arp Address Specification And General Operation
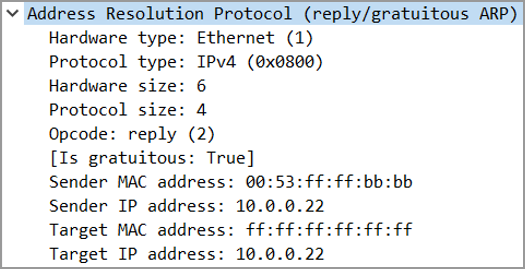
Gratuitous Arp Definition And Use Cases Practical Networking Net
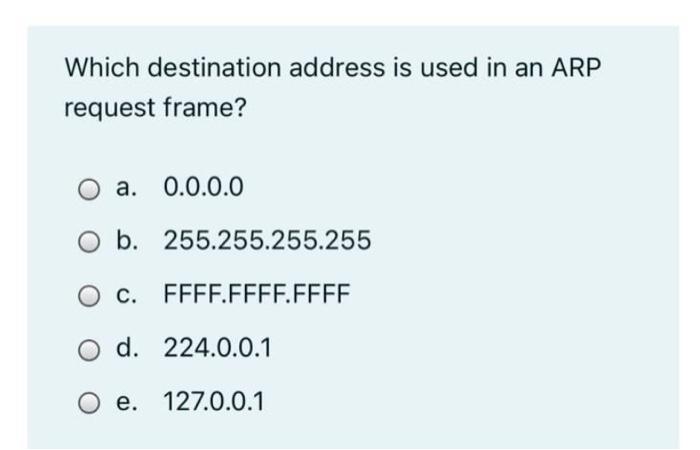
Solved Which Destination Address Is Used In An Arp Request Chegg Com

Belum ada Komentar untuk "Which Destination Address is Used in an Arp Request Frame"
Posting Komentar